Quick Start
This chapter will demonstrate how to use spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config and spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery to complete the configuration management and service discovery of Spring Cloud applications.
Nacos Server
Free Nacos Server On Alibaba Cloud
The easiest way to experience the Spring Cloud Alibaba registration and configuration center is to directly access the hosted Nacos Server on Alibaba Cloud, which eliminates the tedious steps of local installation and download. Please refer to how to experience and access Alibaba Cloud hosted free Nacos Server for details.
If using the cloud hosted version of Nacos Server, replace 127.0.0.1:8848 with the cloud hosted Nacos Server address in the following document.
Start Your Own Nacos Server
For details, refer to the official website of Nacos.
After Nacos Server is started successfully, enter http://ip:8848/nacos in the browser address bar to view Nacos console (default account name and password are nacos/nacos) :
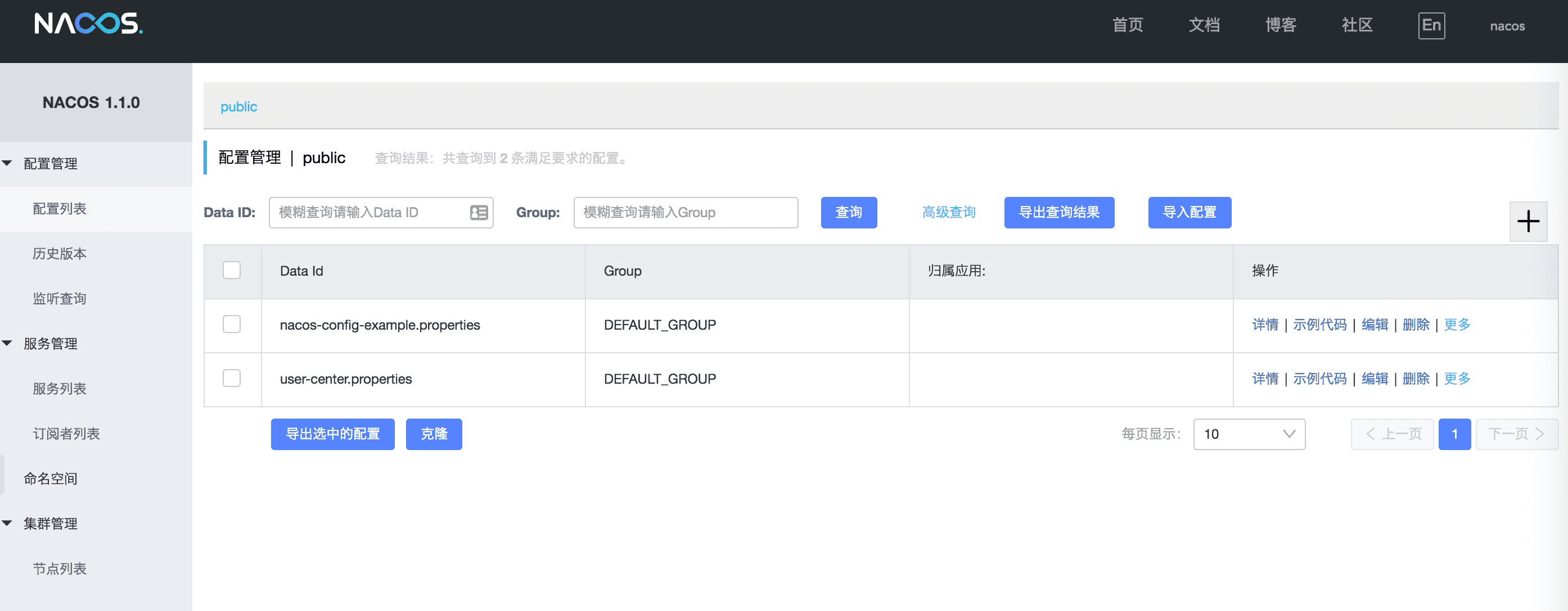
For more Nacos Server version, can from release page to download the latest version.
Nacos configuration center
Access Nacos Config
If you want to use Nacos for configuration management in your project. You need to do the following (ensure that Nacos Server is started)
-
Add a starter whose group ID is com.alibaba.cloud and artifact ID is spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config to the pom.xml file:
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId></dependency> -
The application/src/main/resources/application. The yaml configuration file configuration Nacos Config address and introduce the service configuration:
spring:cloud:nacos:serverAddr: 127.0.0.1:8848config:import:- nacos:nacos-config-example.properties?refreshEnabled=true -
After completing the preceding two steps, the application will obtain the corresponding configuration from Nacos Config and add it to PropertySources in the Spring Environment. Suppose we save part of the Nacos configuration through the Nacos configuration center. There are four examples as follows:
- BeanAutoRefreshConfigExample: through the configuration information for the configuration bean, supporting configuration changes automatically refresh;
- ConfigListenerExample: indicates the listening configuration;
- DockingInterfaceExample: Interconnects with Nacos interface to add, delete, modify and check configuration information through the interface;
- ValueAnnotationExample: Obtain configuration information using the @Value annotation.
Add Nacos configuration
-
Use the CLI
Terminal window $ curl -x POST "http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/cs/configs? DataId = nacos - config - example. Properties&group = DEFAULT_GROUP & content = spring. Cloud. Nacos. Config. ServerAddr = 127.0.0.1:0 8848% Aspring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix=PREFIX%0Aspring.cloud.nacos.config.group=GROUP%0Aspring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=N AMESPACE" -
Console Mode (recommended)
The dataId is nacos-config-example.propertiesgroup is DEFAULT_GROUPThe configuration content is as follows:
Spring.cloud.nacos.config.serveraddr=127.0.0.1:8848spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix=PREFIXspring.cloud.nacos.config.group=GROUPspring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=NAMESPACE
Start the application and validate
Application startup
-
Add other configuration: in application /src/main/resources/application. The yaml add basic configuration information:
server:port: 18084management:endpoints:web:exposure:include: "*" -
Start the application, support IDE directly start, compile and package start:
- IDE Direct startup: Find the main class NacosConfigApplication and run the main method to start the application.
- package and compile startup: First run mvn clean package to compile and package the project, and then run java -jar nacos-config-example.jar to start the application.
Function verification
-
Verify automatic injection
Request http://127.0.0.1:18084/nacos/bean address, it can be seen that the data is successfully obtained from the Nacos collocation center.
Terminal window $ curl http://127.0.0.1:18084/nacos/beanResponse:
{"serverAddr": "127.0.0.1:8848","prefix": "PREFIX","namespace": "NAMESPACE","group": "GROUP"} -
Verify the dynamic refresh
Again request http://127.0.0.1:18084/nacos/bean address, you can see applications have access to the latest data from Nacos.
Terminal window $ curl http://127.0.0.1:18084/nacos/beanResponse:
{"serverAddr": "127.0.0.1:8848","prefix": "PREFIX","namespace": "NAMESPACE","group": "DEFAULT_GROUP"}
Nacos configuration management example source code reference: Nacos configuration management example
For more information about Spring Cloud Alibaba Nacos Config’s advanced features and how to use them, see the Advanced Guide to Registering the Configuration Center section!
Nacos Service Registration and Discovery
Access Nacos Discovery
If you want to use Nacos for service discovery in your project. You need to do the following (ensure that Nacos Server is started).
-
Add a starter with group ID com.alibaba.cloud and artifact ID spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery to the pom.xml file:
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId></dependency> -
Add application configuration: in application /src/main/resources/application properties Nacos Server address that is configured in the configuration file:
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848 -
Use the @EnableDiscoveryClient annotation to enable service registration and discovery:
@SpringBootApplication@EnableDiscoveryClientpublic class ProviderApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class, args);}@RestControllerclass EchoController {@GetMapping(value = "/echo/{string}")public String echo(@PathVariable String string) {return string;}}}
Start the application and validate
Application startup
-
Add configuration: in nacos-discovery-provider-example project /src/main/resources/application.properties. The basic configuration information added to the properties
spring.application.name=service-providerserver.port=18082 -
Start the application, support IDE directly start, compile and package start.
- IDE Direct startup: Find ProviderApplication, the main class of nacos-discovery-provider-example project, and run main to start the application.
- Start after packaging and compiling: Execute mvn clean package in nacos-discovery-provider-example project to compile and package the project. Then run the java -jar nacos-discovery-provider-example.jar command to start the application.
verification
-
Query services
Enter the following command to query the Nacos Server. You can see that the service node has successfully registered with Nacos Server.
Terminal window curl http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/catalog/instances? serviceName=service-provider&clusterName=DEFAULT&pageSize=10&pageNo=1&namespaceId=Response:
{"list": [{"ip": "192.168.3.19","port": 1000,"weight": 1,"healthy": true,"enabled": true,"ephemeral": true,"clusterName": "DEFAULT","serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@service-provider","metadata": {"preserved.register.source": "SPRING_CLOUD"},"instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000,"instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000,"ipDeleteTimeout": 30000}],"count": 1} -
Service discovery
Add the following dependencies in pom.xml:
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-loadbalancer</artifactId></dependency></dependencies>Add the following configurations to the configuration file:
spring.cloud.loadbalancer.ribbon.enabled=falsespring.cloud.loadbalancer.nacos.enabled=true
Service consumption
Application Configuration
This section only covers the Ribbon, RestTemplate, and FeignClient for your understanding of access methods. If other service Discovery components have been used, you can directly replace dependencies to access Nacos Discovery.
-
Add @LoadBlanced annotations to connect the RestTemplate to the Ribbon:
@Bean@LoadBalancedpublic RestTemplate restTemplate() {return new RestTemplate();} -
The FeignClient is integrated with the Ribbon by default. Here is how to configure a FeignClient:
@FeignClient(name = "service-provider")public interface EchoService {@GetMapping(value = "/echo/{str}")String echo(@PathVariable("str") String str);}Wrap the EchoService interface as a FeignClient using the @FeignClient annotation, with the attribute name corresponding to the service name service-provider.
The @RequestMapping annotation on the echo method maps the echo method to the URL “/echo/{str}”, and the @PathVariable annotation maps {str} in the URL path to the echo method parameter str.
-
Inject both into the Controller:
@RestControllerpublic class TestController {@Autowiredprivate RestTemplate restTemplate;@Autowiredprivate EchoService echoService;@GetMapping(value = "/echo-rest/{str}")public String rest(@PathVariable String str) {return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/echo/" + str, String.class);}@GetMapping(value = "/echo-feign/{str}")public String feign(@PathVariable String str) {return echoService.echo(str);}} -
Add necessary configurations:
In nacos-discovery-consumer-example project /src/main/resources/application. The basic configuration information added to the properties:
spring.application.name=service-consumerserver.port=18083 -
Start the application
- IDE direct startup: Find the main class of nacos-discovery-consumer-example project ConsumerApplication and execute the main method to start the application.
- Start after packaging and compiling: Execute mvn clean package in nacos-discovery-consumer-example project to compile and package the project. Then run the java -jar nacos-discovery-consumer-example.jar command to start the application.
verification
-
Request http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-rest/1234 address, You can see that the response displays the message “hello Nacos Discovery 1234” returned by Nacos-discovery-provider-example, proving that the service Discovery is valid.
Terminal window curl http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-rest/1234Response:
hello Nacos Discovery 1234 -
Request http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-feign/12345 address, You can see that the response shows the message “hello Nacos Discovery 12345” returned by Nacos-discovery-provider-example, proving that the service Discovery is valid.
Terminal window $ curl http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-feign/12345Response:
hello Nacos Discovery 12345
Nacos service registration and discovery sample source code reference: Nacos service registration and discovery example
For more advanced features and usage methods of Nacos service registration and discovery, please refer to the registration configuration center advanced guide chapter!



