Quick Start
This chapter will demonstrate the use of @Scheduled Annotate to implement distributed scheduled tasks. @The scheduled annotation is the default implementation of a scheduled task scheduling framework under the spring context, which can implement the scheduled scheduling of a certain method and supports Cron, fixedDelay, and fixedRate expressions.
Access to cloud version
The simplest way to connect to Spring’s distributed scheduled tasks is to directly connect to the Alibaba Cloud hosted Distributed Task Scheduling Platform SchedularX Not only is it fully compatible with Spring @Schedule annotations, but it also features high availability, high security, high performance, maintenance free, and low cost.
The task management platform of the Task Scheduling Platform SchedularX can help you dynamically add, modify, and operate scheduled tasks, as well as enterprise level observable solutions such as alarm monitoring, historical recording, log services, and link tracking, ensuring the stable operation of your scheduled tasks.
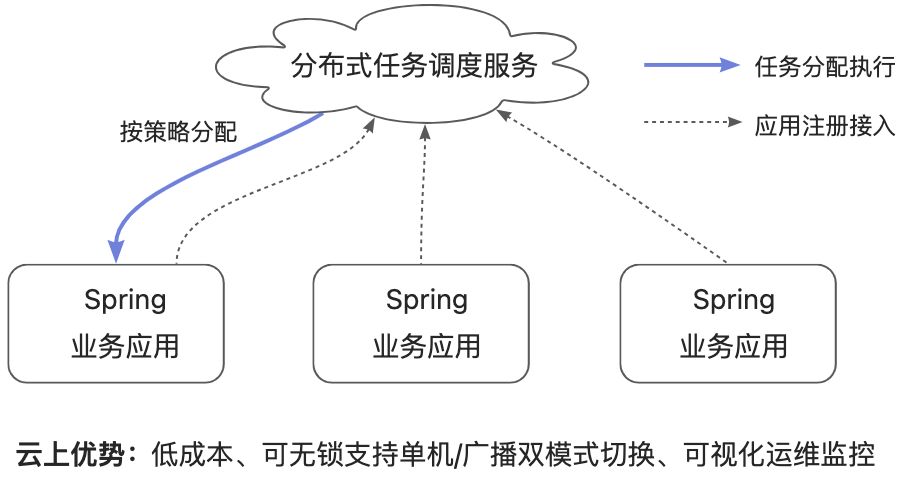
Access steps
- Log in to the SchedulerX Console Open the service for free.
- Reference access document access, each account has 5 free task quotas.
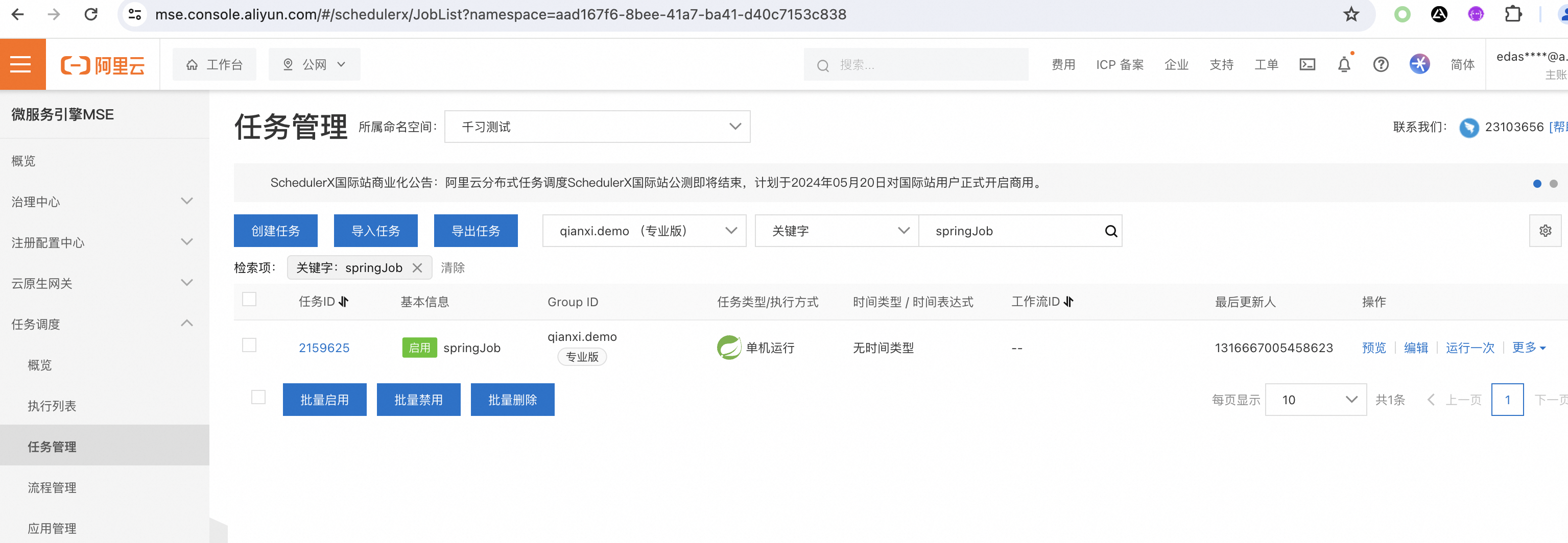
Local access method
Without relying on cloud products, local access methods can be combined with @ Scheduling Lock Annotate to implement distributed scheduled tasks.
@The Scheduling Lock annotation is a framework for distributed locks, combined with the @ Scheduling annotation, to ensure that tasks are executed only once on multiple nodes at the same time. This framework supports the implementation of various distributed locks, such as Jdbc, Zookeeper, Redis, etc. The principle is as follows
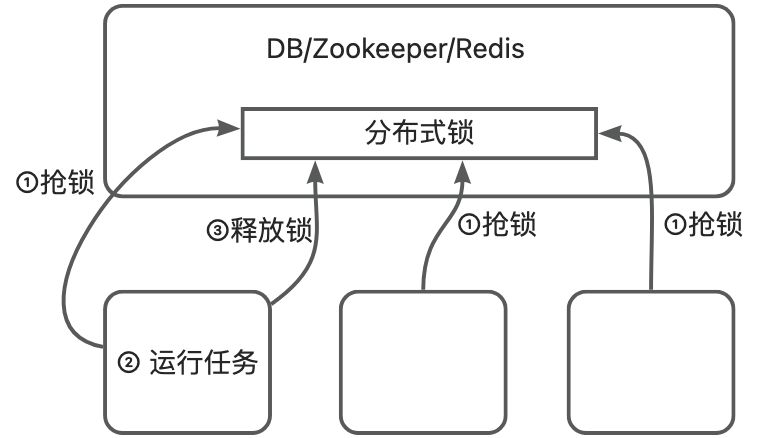
Access steps
Taking MySQL distributed lock as an example, demonstrate the access process of distributed tasks
- Create tables in MySQL
CREATE TABLE shedlock(name VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, lock_until TIMESTAMP(3) NOT NULL, locked_at TIMESTAMP(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3), locked_by VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (name));- Introduce the dependency of shedlock in the pom.xml file
<dependency> <groupId>net.javacrumbs.shedlock</groupId> <artifactId>shedlock-spring</artifactId> <version>4.23.0</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>net.javacrumbs.shedlock</groupId> <artifactId>shedlock-provider-jdbc-template</artifactId> <version>4.23.0</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId></dependency><dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.33</version></dependency>- Add the jdbc configuration in the application.properties file (ignore this step if it has already been added)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/testdb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=falsespring.datasource.username=rootspring.datasource.password=123456spring.datasource.driver-class=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver- Configure LockProvider
import java.util.TimeZone;import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.core.LockProvider;import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.provider.jdbctemplate.JdbcTemplateLockProvider;
@Configurationpublic class ScheduledLockConfig {
@Autowired private DataSource dataSource;
@Bean public LockProvider lockProvider() { return new JdbcTemplateLockProvider(JdbcTemplateLockProvider.Configuration.builder() .withJdbcTemplate(new JdbcTemplate(dataSource)) .withTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC")) .build()); }}- Configure the startup class and enable Scheduling Tasks
@SpringBootApplication@EnableScheduling@EnableSchedulerLock(defaultLockAtMostFor = "3m")public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args); }}- Create scheduled tasks
import org.joda.time.DateTime;import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import net.javacrumbs.shedlock.spring.annotation.SchedulerLock;
@Componentpublic class SpringJob {
/** * 每5分钟跑一次 */ @Scheduled(cron = "0 */5 * * * ?") @SchedulerLock(name = "SpringJob.job1", lockAtMostFor = "2m", lockAtLeastFor = "1m") public void job1() { System.out.println("time=" + DateTime.now().toString("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " do job1..."); }
/** * 每5秒跑一次 */ @Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) @SchedulerLock(name = "SpringJob.job2", lockAtMostFor = "4s", lockAtLeastFor = "4s") public void job2() { System.out.println("time=" + DateTime.now().toString("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " do job2..."); }
/** * 上次跑完之后隔5秒再跑 * @throws InterruptedException */ @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000) @SchedulerLock(name = "SpringJob.job3", lockAtMostFor = "4s", lockAtLeastFor = "4s") public void job3() throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("time=" + DateTime.now().toString("YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") + " do job3..."); Thread.sleep(10000); }
}


